M.E. Benítez, C. Prezzi, C.A. Ballivián Justiniano, S.O. Verdecchia, F.J. De Martino, M. Carlini, M.E. Lanfranchini
2 023
Journal of South American Earth Sciences Volume 121 , January 2023
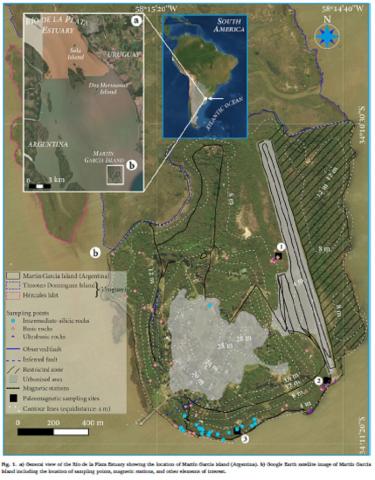
The Martín García Complex, which crops out at the homonymous island of the Río de la Plata Estuary, is composed of intermediate to silicic orthogneisses and granitoids, hornblende and olivine gabbros, and felsic dykes of Paleoproterozoic and Mesoproterozoic ages, as well as serpentinized ultrabasic rocks of unknown age. A major part of this igneous-metamorphic basement is covered by sediments and vegetation, hiding the relationships between the different rock units, and hindering their study. Therefore, a ground magnetic survey and the consequent 3D geophysical modeling were conducted to elucidate the geometry of the ultrabasic bodies in the subsurface. Normal and reverse dipolar sub-circular and elongated (∼ENE-WSW) magnetic anomalies were identified. It is proposed that Cr-rich spinels would be responsible for some of the detected magnetic anomalies. Our results suggest the existence of three magnetic units with a dyke-type geometry, all of them with ∼ENE-WSW trend and steep dip. The magnetic survey and 3D modeling allowed us to confirm the continuity and extension in the subsurface of the ultrabasic bodies cropping out discontinuously on the surface. According to their crosscutting relationships, a post-Stenian age is proposed for these rocks. Magnetic patterns identified in Martín García Island are similar to those observed in western Uruguay, suggesting that the Martín García Complex would be part of the Piedra Alta Terrane (Río de la Plata Craton).