P.R. Franceschinis, J.W. Afonso, M.J. Arrouy, L.E. G´omez-Peral, D. Poiré, R.I. F. Trindade, A.E. Rapalini
2 022
Precambrian Research 383 (2022)
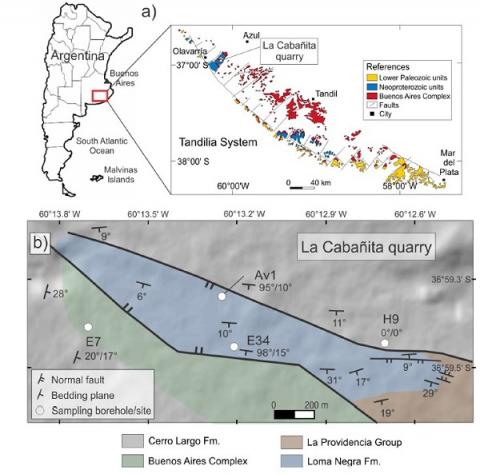
A paleomagnetic and rock magnetic study was carried out in the Ediacaran Avellaneda (~570 Ma) and Cerro Negro (~555 Ma) Formations belonging to the La Providencia Group, in the upper part of the Neoproterozoic sedimentary cover of the Tandilia region, in the Río de la Plata craton. The Avellaneda Formation was studied at outcrop level and in three drill cores, yielding a mean characteristic remanence direction of Dec: 21.4◦, Inc: 67.1◦, α95: 4.2◦, k: 23.9, N: 51 and a paleomagnetic pole at 1.0◦ S, 313.4◦ E, A95: 5.9◦. The Cerro Negro Formation yielded a mean characteristic direction of Dec: 22.0◦, Inc: 68.5◦, α95: 10.3◦, k: 20.8, N: 11 obtained from a single drill core, from which a paleomagnetic pole at 3.6◦ S, 307.8◦E, A95: 16.6◦ was computed. Rock magnetic data indicates that magnetic remanence is mainly associated with magnetite and hematite. The paleomagnetic information presented here results in a change in the previously accepted Late Ediacaran apparent polar wander path of the Río de la Plata Craton. The newly obtained poles indicate that Río de la Plata Craton experienced a rapid drift from a low latitudes location (ca. 19◦ S) at ca. 600 Ma to moderately higher latitudes (between 50◦ and 42◦S) from around 580 to 550Ma.